Product Development Life Cycle Definition
The Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) is a comprehensive series of steps that a product undergoes, starting from its initial conception to its eventual introduction in the market.
This life cycle is critical in shaping the trajectory of a new product, as it meticulously outlines each phase of development, ensuring thorough consideration and refinement at every stage.
In essence, PDLC is structured to guarantee that products undergo rigorous design, development, and testing processes. This ensures they not only meet the envisioned specifications but are also aligned with user expectations and market demands. It minimizes risks, addresses issues early, and incorporates feedback.
Each stage of the Product Development Life Cycle holds significant importance. By adhering to the principles of PDLC, businesses can optimize their development processes, ensuring that the end product is not only robust and functional but also resonates with the target audience.
Through this detailed approach, companies can enhance their market presence, build brand credibility, and drive long-term success by introducing products that truly make a mark.
In the digital era, where consumer expectations and industry standards are ever-evolving, a well-structured Product Development Life Cycle is indispensable. It acts as a blueprint for innovation, guiding companies in navigating the complexities of product creation and positioning them to meet and exceed the dynamic needs of the market.
What is Product Life Cycle?
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a fundamental concept in marketing that outlines the progression of a product through four distinct stages. These stages are Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline, each characterized by unique shifts in sales, profits, and competitive dynamics.
During the Introduction stage, a product makes its debut in the market. This phase is marked by initial challenges such as low sales volume and high distribution and promotion expenses, aiming to establish its presence and create awareness. The primary goal during this stage is to build a market for the product.
As the product gains traction, it enters the Growth stage, characterized by rapidly increasing sales and growing profits. This is a pivotal time for market share acquisition, as consumer awareness expands and brand preference solidifies. During this stage, competition tends to intensify, and companies might invest in enhancing the product features or expanding the product line to sustain the momentum.
The Maturity stage follows, where the product reaches its peak in market saturation. At this juncture, sales growth starts to slow down, and profits stabilize. This stage presents a challenge for businesses to differentiate their products from competitors and maintain market share through strategic pricing, promotional activities, and efficiency improvements.
Finally, the product reaches the Decline stage, marked by a decrease in sales and shrinking market share. This decline could be attributed to factors such as technological advancements, shifts in consumer preferences, or increased competition. Companies, at this point, must decide whether to discontinue the product, innovate, or find new uses and markets to prolong the product’s life.
By effectively managing each stage of the PLC, companies can optimize profits, make informed investment decisions, and align product strategies with market realities, ensuring sustained business success in a competitive landscape.
MORE: Product launch: Everything you need to know
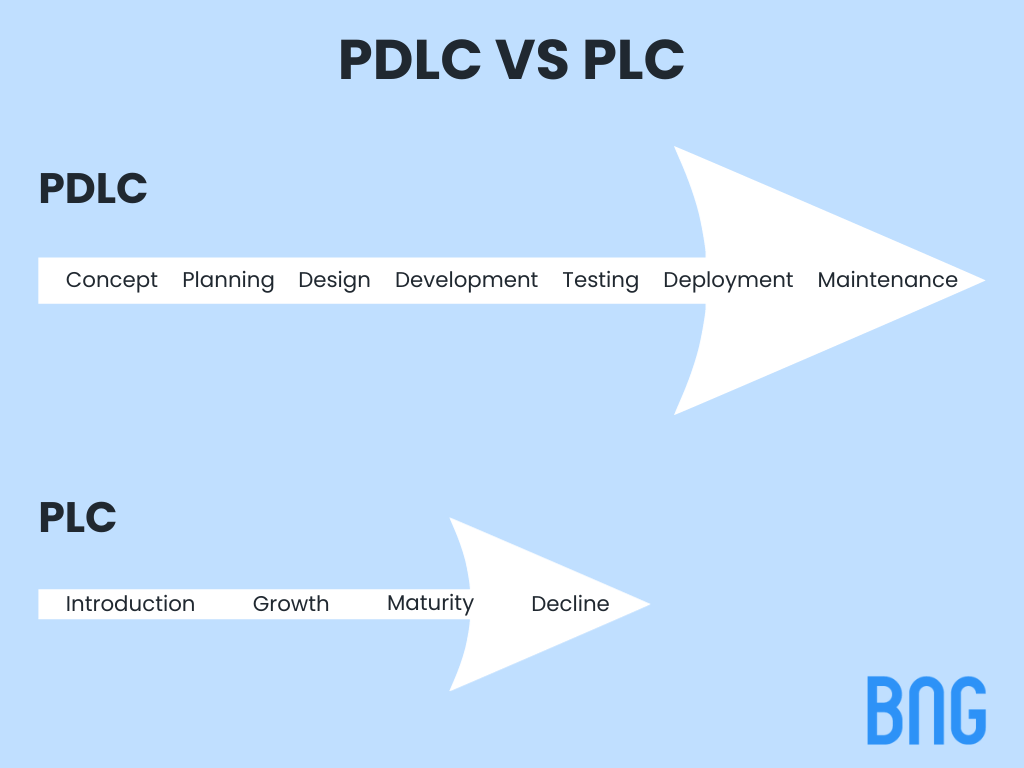
Product Development Life Cycle vs Product Life Cycle
While they may seem synonymous due to their names, these two life cycles serve different purposes and encompass different stages in a product’s journey from conception to discontinuation. PDLC focuses on the development process, ensuring the product is market-ready, whereas PLC tracks the product’s performance and longevity in the market.
| Aspect | Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) | Product Life Cycle (PLC) |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | To develop a new product or enhance an existing one through various stages including idea generation, development, testing, and launch. | To manage and optimize a product’s journey from market introduction to decline, focusing on maximizing profits and market presence. |
| Stages Involved | Concept, Planning, Design, Development, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance. | Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline. |
| Focus | Development of the product, ensuring it meets market needs and is of high quality. | Market performance, including sales, market share, and competition, throughout the product’s presence in the market. |
| Duration | Typically until the product is launched. | Spans the entire life of the product, from launch to discontinuation. |
| Decision Making | Decisions revolve around product features, design, development methods, and testing protocols. | Decisions focus on marketing strategies, pricing, product variations, and potential redevelopment or discontinuation. |
PDLC vs. SDLC: What’s the Difference?
Both the Product Development Life Cycle (PDLC) and the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provide structured frameworks for the development and realization of products and systems.
While PDLC can be applied to the development of any product, SDLC is specialized for software development, focusing on stages specific to software creation.
Understanding the differences between these two life cycles is crucial for anyone involved in product or software development as it helps in selecting the appropriate model for successful project execution.
| Aspect | PDLC | SDLC |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Encompasses the development of any product. | Exclusively focused on software development. |
| Applicability | Applies to various industries such as manufacturing, technology, etc. | Pertains mainly to the IT and software industry. |
| Stages Involved | Idea generation, development, testing, and launch. | Planning, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. |
| End Product | Can be a tangible product or a software/application. | Software or application. |
| Goal | To bring a new product or an enhanced version of a product to market. | To develop functional software to meet specific requirements. |
| Focus Areas | Market research, prototyping, design, development, user acceptance testing, and market launch. | Requirements analysis, software design, coding, testing, integration, and maintenance. |
Thinking of introducing a new product to the market but can’t seem to find the perfect name for the product launch? Try our product name generator and discover thousands of potential names in just a few seconds.
What are Product Development Life Cycle Stages
The stages are:
- Idea Generation,
- Idea Screening,
- Concept Development and Testing,
- Business Analysis,
- Product Design and Development,
- Testing and Market Testing,
- Commercialization, and
- Evaluation of Results.
A deep dive into each of these stages reveals the complexity and significance of every step, underlining the importance of strategic execution for achieving product success in today’s dynamic market.
MORE: What is product development?
Factors That Affect Product Development Life Cycle
Numerous factors have the potential to impact the Product Development Life Cycle, thereby influencing the overall trajectory of a product from its conceptualization to its realization in the market.
Market demand, technological advancements, competition, and organizational resources are all important factors. The fluctuations of market demand can alter the landscape, dictating the need for adaptability and innovation.
Technological advancements continually redefine possibilities, setting new standards and expectations. Competition fuels the drive for differentiation and excellence, while organizational resources, both human and financial, form the backbone of the development process.
Recognizing and navigating these factors are paramount for businesses aiming to streamline their product development, mitigate risks, and strategically position their offerings in the increasingly competitive and evolving market.
Key Takeaways
In this article, we’ve delved into the definitions of the PDLC (Product Development Life Cycle), PLC (Product Life Cycle), and SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle), as well as their comparisons.
By understanding the distinctions between each of the cycles, businesses and professionals can better align their strategies and methodologies to the specific challenges and requirements of their projects.
This knowledge enables more informed decision-making, fosters efficient resource allocation, and ultimately drives more successful product and software outcomes.