What Is a TLD?
A top-level domain (TLD) is the final part of a domain name that comes after the dot.
For example, in businessnamegenerator.com, the top-level domain is .com. TLDs are top-level as they are at the highest hierarchical level in the domain name system (DNS) right after the root domain.
Top-level domains are essential for how DNS servers communicate during the lookup process. They are also important for classifying domain names and letting users understand the website’s purpose.
Why Are TLDs Important?
- TLDs are essential to establishing a domain name. They let users know what type of content they can expect, and they can help you set up clear brand messaging.
- Choosing an unknown TLD can damage your reputation and discourage users from visiting the website.
- Generally, .com domains are regarded as the most trusted and memorable ones.
- However, picking a TLD that’s relevant to your niche can help you establish an authority. If you choose a non-.com domain, make it clear in your advertising.
Example:
Let’s say I want to start a business named StarHive. People have heard about my company and want to visit my website but don’t know the domain name. The majority will assume it’s starhive.com.
If there’s already a website on that domain name that doesn’t belong to me, that can prove bad for my business. That’s why I’d need to advertise my TLD as well.
What Is the Purpose of a TLD?
A fully-qualified domain name consists of three domain name levels:
- Top-level domain: This is also known as an extension.
- Second-level domain: The unique part of the domain name that you choose. You can use your business name or a keyword that will help you direct traffic to your website.
- Third-level domain: Comes before the first dot in the name. They either refer to subdomains or the website host (usually www).
When we talk about domain types, we refer to top-level domains as they show the purpose of a website in advance. These signals can differ from practical and technical standpoints.
For instance, the .hr TLD communicates to DNS servers that the website is from Croatia, but many staffing agencies and HR companies use it as a branding tool.
Types of Top-Level Domains
TLD classification may vary depending on the source, but this is the most popular breakdown of TLD types:
- Generic top-level domains (gTLDs): They are the most recognizable and widely used. gTLDs can represent a specific industry or notation. For example, .net is short for network, .com for commercial, and .org for organization.
- Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs): Containing only two letters, these domains represent countries. Recently, some ccTLDs have become generic and a branding technique (e.g., AI companies use Anguilla’s ccTLD: .ai).
- Internationalized country code top-level domains (IDN ccTLDs): Domains dedicated to websites that use a non-Latin script, such as Chinese, Japanese, and Arabic.
- Test top-level domains (tTLDs): These are used to test website updates and build documentation. You can’t use a tTLD to create a public website.
Most Popular Top-Level Domains
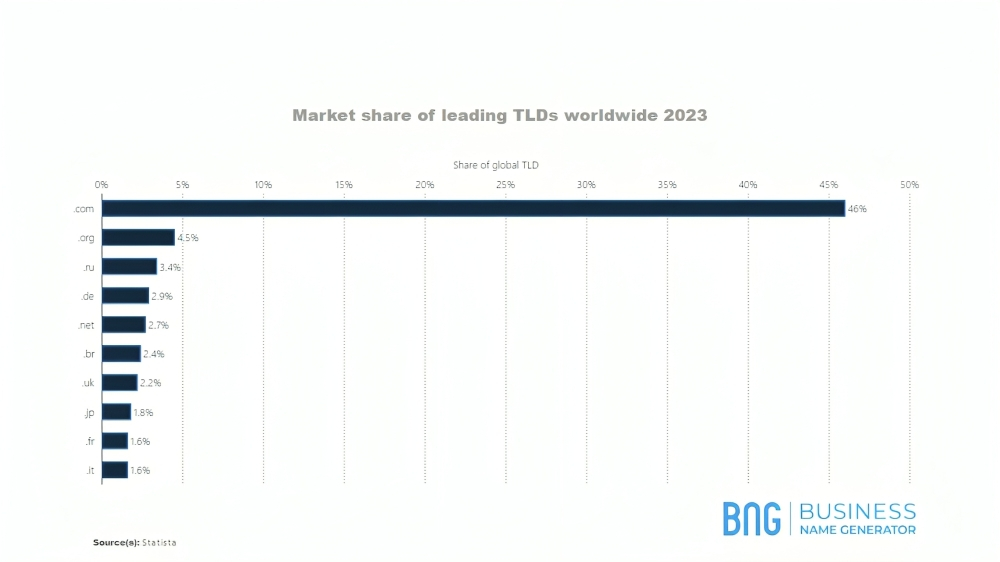
By far the most popular TLD is .com. While .com stands for company, non-business entities also use the extension as their preferred one.
According to Statista, over 46% of all websites use .com.
MORE: Most expensive domain names
Top-Level Domain Examples
There are over 1,500 top-level domains available. As a business owner (or individual), you can’t choose all of them as some have limited uses. For example, .mil is used only for domain names owned by the U.S. military, whereas you need to prove you’re a citizen or resident of the United States if you want to use .us.
Check out the table below to learn what the most popular TLDs are from each type:
| Types of Top-Level Domain | Examples |
|---|---|
| gTLD | – .com, – .net, – .org, – .gov, – .biz. |
| ccTLD | – .us, – .de, – .it, – .fr, – .es, – .cn. |
| IDN ccTLD | – .укр, – .ελ, – .中国, – .გე. |
| tTLD | – .example, – .localhost, – .test. |
Trending Top-Level Domains
According to DNIB.com, Q4 2023 closed with 359.8 million registrations. With generic and country-code TLDs getting oversaturated, the domain name market had a need for an expansion of domain types, which led to new top-level domains (nTLDs).
These nTLDs have a more specific purpose, such as targeting a specific location or region (.africa or .nyc), type of content (.meme or .lgbt), and industry (.tech or .attorney).
The most popular generic nTLDs are .xyz and .online, with a 10.4% and 9% share of all generic nTLDs, respectively. Regarding geographical nTLDs, the leaders are .lat (14.5%) and .tokyo (13.7%). In general, nTLDs combined for 32.6 million domain name registrations (9.07% of all registrations) as of Q4 2023.
Check out the top ten nTLDs currently in use:
[florishdata id=”17062099″ class=”flourish-chart”]
MORE: Domain name trends
Untrustworthy TLDs
Additionally, make sure you avoid TLDs that are associated with spamming and malware scams. While your website might be perfectly safe, people will avoid visiting it, and it can negatively affect your SEO ranking.
Here are the most untrustworthy TLDs according to the Cybercrime Information Center:
[florishdata id=”17138480″ class=”flourish-chart”]
How TLDs Affect SEO
Technically speaking, TLDs don’t affect SEO, with Google and other search engines trying to recommend top-quality content regardless of the domain name it comes with.
Still, they indirectly affect your SEO ranking through people’s perception and likeliness to visit a website. With .com being the most trustworthy, yourBusiness.com will likely get more clicks than yourBusiness.link.
Using a ccTLD can help you with geo-targeting and improve buyer confidence if you want to sell your product or service in a specific location. For example, if you want to sell shoes in Mongolia, you’ll be more successful with shoes.mn instead of shoes.ca.
How to Choose the Best Top-Level Domain
While you can always transfer your website to another domain name, you’ll lose customers’ familiarity and your SEO ranking when doing so. That’s why it’s important to choose the best name right in the beginning and stick with it as long as possible.
When picking a domain name, you should take the following steps:
- Dot-com domains reign supreme and should be your go-to choice,
- If they’re unavailable, opt for a TLD that represents your website and business,
- Think of what your website will be about,
- Use ccTLDs as keywords for a specific industry or type of content.
Once you make your decision, it’s time to register your domain name. Check out our video below to learn more about the process:
Consider Getting Multiple TLDs
There are several multiple reasons why you should get more than one domain name, i.e., multiple domain types with the same name (e.g., yourBusiness.com, yourBusiness.net, and yourBusiness.co). This allows you to determine which one works best and attracts the most users.
Additionally, it protects you from competitors that might try to cybersquat, i.e., use a similar domain name to trick your customers into buying their products.
The ccTLD Industry and Branding Examples
As we’ve said, some ccTLDs have become generic and associated with specific industries and branding. Here are some of the examples of gccTLDs:
| ccTLD | Original Country | New Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| .it | Italy | IT companies |
| .fm | Federated States of Micronesia | Radio stations |
| .tv | Tuvalu | Television and streaming services |
| .me | Montenegro | Personal blogs and brands |
| .ai | Anguilla | Companies working with artificial intelligence |
| .hr | Croatia | HR companies and staffing agencies |
| .io | British Indian Ocean Territory | Tech and SaaS companies |
Takeaway Points
Aside from the technical intricacies, top-level domains have an important purpose in your online branding. Depending on which TLD you use, it can drive traffic to your website, or people may avoid clicking on your links regardless of what you offer.
The .com extension is by far the most popular one, but you don’t have to go with it, and a different TLD might be a better choice for your business.
If you need help choosing a domain name (with its extension), use our AI-powered domain name generator. It will create 1,000s of name ideas and automatically check domain name availability for various extensions.