Subdomain Definition
A subdomain is an extension of your domain name that can help you organize and categorize different sections of your website. You can use multiple subdomains to create varying structures and content hierarchies under the same domain name.
For example, it allows you to create an online store with a different layout from your blog.
What Does a Subdomain Look Like?
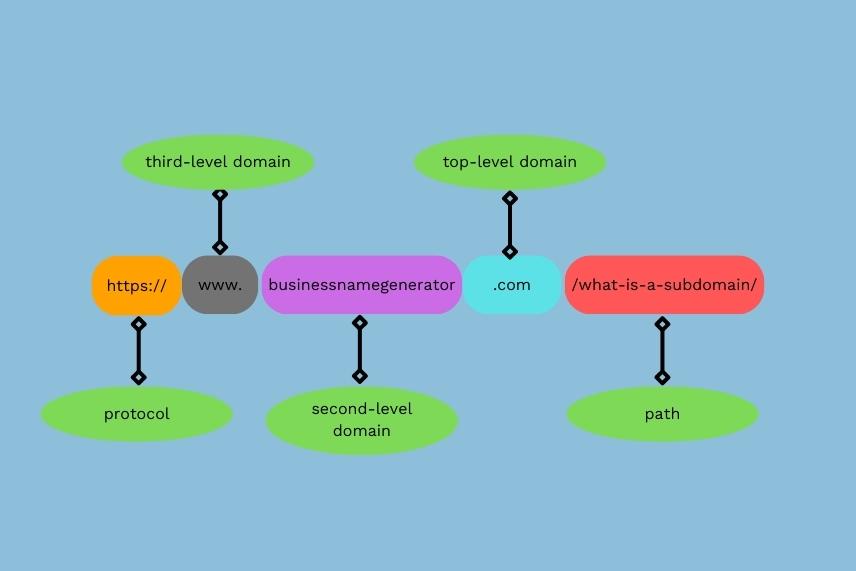
Before getting into subdomains, we must understand domain names and their structures. When you visit a URL, you’ll see it consists of several elements separated by a dot or a slash.
For example, if you check out the URL you’re currently on, you’ll read https://www.businessnamegenerator.com/what-is-a-subdomain/. Its elements are as follows:
- https:// – Protocol that allows data to travel between a web server and your browser.
- www – Known as the third-level domain, it usually refers to the website’s host.
- businessnamegenerator – This is the unique part of your domain name (called the second-level domain).
- .com – Top-level domain (TLD, or extension) that can provide information about the geographic location, type of content or website purpose. Some of the most common TLDs are .com, .net, .us, and .co.
- what-is-a-subdomain – Called a path, shows the exact location of a specific page or post you’re on.
When you choose a domain name, you have to pick a name and domain type that you can’t change later on. The only thing you can edit is the third-level domain, often known as a subdomain. For example, instead of having www.domainName.com, you can have shop.domainName.com.
What Is a Subdomain in a URL: Image
MORE: Who owns a domain name
What Is a Subdomain Used For?
Companies commonly use subdomains for two reasons:
- Content organization: It lets users know what section of the website they’re on and what they can expect to get or learn. As a website manager, you can use subdomains to create different content hierarchies (i.e., how you arrange information).
- Testing: Website admins use subdomains only they can access to test out new designs and backend updates before they make them public.
We chatted with David Barnett, Brand Protection Strategist at Stobbs, on the topic of subdomains, and he had this to say: “In legitimate use, subdomains can serve a range of purposes, such as allowing the creation of individual microsites for sub-brands or campaigns, or the production of region- or subject-specific subsites.”
Barnett continued, “However, subdomains can also be abused in the construction of infringements. Examples might include cases where a brand name is utilized in the production of a deceptive URL or the construction of a site incorporating a brand infringement or a potentially unauthorized claim of affiliation.”
What Is a Subdomain for a Website?
Let’s imagine I’m a popular digital artist. People know about me because of your successful website, milossoro.com.
Now, I want to sell my art, but I’ve decided I need a separate website homepage with a different design, menu buttons, and so on. All similar domain names are taken, so I have to choose between a dodgy domain type or a name nobody will remember.
That’s where subdomains come in. I can use my established domain name to create store.milossoro.com and a new website. You can also add a separate WordPress installation on your subdomain and create an online store from scratch.
MORE: Learn how to buy a domain name.
What Is a Subdomain Example?
Check out some of the most popular subdomain examples and their uses:
| Subdomain Use | Explanation | Subdomain Examples |
|---|---|---|
| eCommerce | Using a separate subdomain can help you install specialized functionalities, such as managing transactions. | – store.yourDomain.com, – shop.yourDomain.com, – buy.yourDomain.com, – deals.yourDomain.com. |
| Mobile | A subdomain dedicated to mobile users; it allows you to use a design made for mobile interfaces and optimized for user experience on smaller devices. | – m.yourDomain.com, – mobile.yourDomain.com, – msite.yourDomain.com, – touch.yourDomain.com. |
| Blog | With a blog subdomain, you can target keywords and discuss topics different from your main site. | – blog.yourDomain.com, – journal.yourDomain.com, – learn.yourDomain.com, – resources.yourDomain.com. |
| Support | It allows you to create dedicated support platforms for your customers. | – support.yourDomain.com, – contact.yourDomain.com, – help.yourDomain.com, – helpdesk.yourDomain.com. |
| Location | Great for creating geo-specific content and displaying local store options. | – us.yourDomain.com, – uk.yourDomain.com, – tokyo.yourDomain.com, – it.yourDomain.com. |
| Language | If you run a website in several languages, you can use subdomains to keep them separate. Wikipedia is a great example of language subdomain use. | – en.yourDomain.com, – it.yourDomain.com, – fr.yourDomain.com, – pt.yourDomain.com. |
| Audience | You can create platforms with varying levels of permissions for your users. Some websites, such as Medium.com, allow you to create your own subdomain and display your content there. | – developers.yourDomain.com, – student.yourDomain.com, – username.yourDomain.com, – users.yourDomain.com. |
| Forum | You can keep your community neatly organized with a dedicated subdomain for forums and discussion boards. | – forum.yourDomain.com, – community.yourDomain.com, – ask.yourDomain.com, – discussion.yourDomain.com. |
Pros and Cons of Subdomains
As with any other decision, choosing to set up a subdomain comes with its pros and cons, and you should weigh your options before creating a subdomain structure.
Pros
- Subdomains are great for maintaining your brand positioning and using its recognition. If people know about your website, they’ll automatically see the connection between it and the subdomain.
- Allow you to streamline your website and offer better onsite navigation.
- SEO benefits, such as building authority and less concerns about keyword cannibalization.
- Cost and resource management. David Barnett commented, “It allows for a reduction in cost and resource, compared to that required to register, manage and secure large numbers of additional official domains, and keeps all content consolidated under a single domain name.”
Cons
- Running subdomains requires putting in extra work.
- Navigating between subdomains can be difficult, negatively affecting user experience.
- Becoming your own competitor if you’re not careful about your content strategies.
- Security and vulnerability issues. Barnett noted, “Extensive use of subdomains also requires careful management. For example, if subdomains are not deactivated when no longer required, they can potentially become a point of vulnerability to hijacking and re-direction to threatening content (exploitation of so-called ‘dangling’ DNS records).”
Subdomains vs. Subdirectories
Subdomains are not the only way to structure your website content; you can also use subdirectories. Unlike subdomains that come before the domain name, subdirectories come after. For instance, the word blog can be used as a:
- Subdomain: blog.yourDomain.com,
- Subdirectory: www.yourDomain.com/blog.
Essentially, think of subdomains as separate hardware drives on your computer, while subdirectories are folders on the same drive.
Check out the table below to learn more about the differences between the two:
| Subdomains | Subdirectories |
|---|---|
| Search engines see them as separate websites. | They are part of the main website. |
| They have an independent SEO ranking. | You can benefit from established backlinks and authority. |
| You have to build up your SEO from scratch. | Subdirectories can’t be used as independent entities. |
| You must be in line with content from other subdirectories. |
Are Subdomains Bad for SEO?
When using subdomains, your overall SEO authority may disperse, since Google treats them as separate entities from main domains. Building an SEO ranking from scratch is difficult, especially when you can’t rely on existing backlinks.
Subdirectories let you build on your existing SEO efforts, but they come with technical limitations, such as using the same DNS server and not having a dedicated platform.
Subdomain Cannibalization
One of the main benefits of subdomains is that you can use them to focus on a particular set of keywords.
This way, Google understands your site’s focus, and you’ll be able to build a strong niche authority without facing the risk of keyword cannibalization.
When it comes to using subdirectories, you make it easier for Google to crawl subfolders, tracking analytics is more efficient, and you can benefit from internal linking.
If you’re not sure that having an independent entity with its own SEO ranking is crucial, using subfolders is more efficient and may be the better choice for you.
How to Create a Subdomain
So, what is needed to create a subdomain? You only need a registered domain name and access to your registrar’s dashboard.
Creating a subdomain will depend on the domain registrar or hosting provider you use. Still, the process should be similar and easy to complete. Check out how the process works for some of the most popular registrars:
| GoDaddy | Hostinger | Domain.com | Namecheap |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Sign in to your GoDaddy account, 2. Select the domain you want to add a subdomain to, 3. Choose the DNS tab, 4. Under DNS Records, select Add New Record, 5. Choose A from the Type menu and enter the subdomain name, 6. Save the new record. | 1. Log in to your account and visit the Websites section, 2. Click on Manage next to the domain of choice, 3. Find and click on Subdomains in the Domains section, 4. Press Create a New Subdomain and enter its name, 5. Click Create. | 1. Log in to your Domains dashboard, 2. Select the chosen domain and press Manage (in Card view) or the gear icon (in List view), 3. Choose Pointers & Subdomains, 4. Press Add Subdomain, 5. Add the subdomain name and click Save. | 1. Log in to your account and visit the Domain List section, 2. Click Manage next to the domain you want to use, 3. Select the Advanced DNS tab, 4. Press Add New Record, 5. Choose A Record for Type and enter the subdomain name, 6. Click Save All Changes. |
New subdomains can take between 30 minutes and 48 hours to become available.
Don’t know how to pick a registrar? Check out our video guide on where to buy a domain name:
Takeaway Points
A subdomain is a great organizing tool for your website. For example, if you run an eCommerce store, managing transactions becomes important only during the purchasing process. With a shopping subdomain, you wouldn’t need transaction functionality to clutter your main website.
Search engines treat subdomains as separate websites, meaning that you’ll need to start your SEO from scratch. Before you choose to use subdomains, make sure you have a good reason for it and weigh all the pros and cons.
Regardless of how many subdomains you have, users will still recognize you by your main domain name. It needs to be easy to remember, spell, and in line with your brand identity. If you’re having trouble coming up with a high-quality domain name, use our AI-powered domain name generator for free.